This is a guest review by Tom Houseman.
As abortion has become more accepted and less taboo in mainstream America—despite Republican lawmakers doing everything they can to appeal Roe v. Wade—films about pregnancies have had difficulty depicting its characters talking about or even considering abortion. If the movie is about pregnancy, and the journey that the characters take during the course of the pregnancy, then abortion would erase not just the main conflict, but the entire plot of the movie. You would be left with a twenty minute film about characters who neither grew nor changed, because we all know that having babies makes everyone into better-adjusted and more-fulfilled people. In 2007, two American comedies failed spectacularly in realistically addressing the issue of abortion, while a Romanian drama delivered one of the most stark and honest portrayals of a woman obtaining an illegal abortion.
Juno and Knocked Up were two of the biggest comedy hits of 2007, while 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days was completely ignored outside of the arthouse circuit. But both comedies not only do an awful job of treating abortion in a realistic manner, they completely ignore the privilege that their characters have, privilege that not only allows them to consider having a safe, legal abortion, but to decide instead to carry the fetus to term. Every decision that their protagonists make is driven by completely unacknowledged privilege, whereas the decisions that the protagonists of 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days make are greatly influenced by their lack of privilege. By comparing Juno and Knocked Up to the Romanian drama 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days, we see the enormous, and largely overlooked, impact that privilege has on both the decision to have an abortion and the decision not to.
 |
| Alison shopping for the baby in Knocked Up |
Knocked Up gives the most half-assed head nod to the idea of abortion possible and does not remotely recognize the role that class privilege plays in the decision to have a child. The protagonists of Knocked Up are Alison, an uptight TV producer who lives with her sister, and Ben, an unemployed, undocumented Canadian immigrant who spends his days getting stoned with his friends. The two meet at a bar and engage in a drunken one-night stand that, due to a communication error, does not involve contraception. When Alison discovers that she is pregnant, she is faced with a serious decision… kind of… but not really.
The idea of abortion is lazily floated in two scenes adding up to maybe a minute of the two-hour film. The only remarkable thing about these scenes is that throughout both of them nobody actually says the word “abortion.” While Ben bemoans his bad luck at having gotten a woman pregnant after deciding to have unprotected sex with her, his friends suggest plans of action. When Jonah makes the obvious suggestion that Alison simply “take care of it,” Jay is so outraged and offended by the mere idea of abortion that he refuses to let anyone say the word. From then on, Jonah says that what Alison should do “rhymes with shmushmorshmin.” Jay apparently is fine with people having premarital sex, but has deep moral conviction only when it comes to people dealing with the consequences of premarital sex.
Alison also has a very brief conversation about abortion with her mother, who makes very valid points about the impact it will have on Alison’s career. Even though Alison’s mother believes that Alison should get an abortion, saying that having the child would be “a big, big mistake,” she too does not say the word, also using the euphemism “take care of it.” Alison’s conversation with her blunt, critical mother is contrasted by the conversation Ben has with his jovial and supportive father. Ben’s father calls the pregnancy “a blessing,” and the implication is that his upbeat attitude is vastly preferable to Alison’s mother’s negativity.
Do we ever see Alison’s perspective on the issue? What are her thoughts on abortion, both as a legal concern and a personal one? Considering she seems like the type of person who had planned out her entire life, had she planned on having children, and if so, when? We do not see Alison deal with any of these questions, nor does she explain how or why she came to the decision to have her baby. Between the homophobic mockery and the jokes about how uptight and controlling women are, there is no room for serious discussion about abortion.
Nor, of course, is there room for Alison to acknowledge the privilege that goes in to making her decision. Despite not having her own apartment or house, Alison is very well off. She has a very well paying job that gives her financial freedom, a luxury that depressingly few in the United States have. In the flash of a second that abortion is considered, never is the question of whether or not Alison can afford the operation raised, likely because her job gives her health insurance that would cover such a procedure. The cost of raising a child is similarly never considered as a serious issue. Alison buys numerous books and various supplies without ever checking price tags or hunting for bargains. At one point, her sister Debbie offers to buy her a $1,400 crib without batting an eyelash.
In addition, Alison mentions that her employer, E!, will give her three months of paid maternity leave, so she will be able to give birth and care for her baby without having to worry about how she can afford to feed and clothe her newborn child. Alison is fortunate enough to work for a company with at least fifty employees, and to have been employed by them for at least a year. Otherwise she would not qualify for the Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993 mandate which requires companies to provide paid maternity leave for employees who meet the above conditions. This is just one of the many privileges that grant Alison the freedom to choose whether or not to abort her child without fear of any serious consequences except for “sacrificing [her] vagina.”
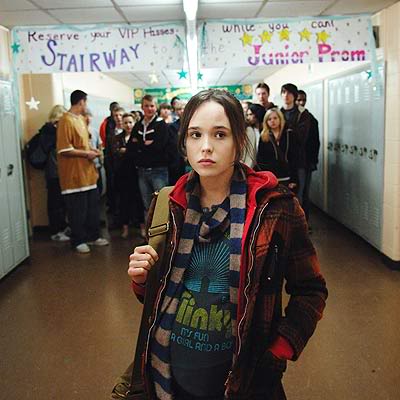
Juno tells a very different story about pregnancy, but still creates a remarkably ideal situation for its protagonist to make the issue of abortion and childbirth seem easier and free of life-changing repercussions. Juno is the eponymous protagonist of the film who, after losing her virginity, discovers that she is pregnant. Unlike Knocked Up, Juno spends a considerable amount of time debating whether or not abortion is the right decision for its protagonist to make, and gives us some insight into her thought process. The first person that Juno tells about her pregnancy is her friend Leah, and in the conversation that they have they both work under the assumption that Juno is going to abort the fetus. Compared to other teen pregnancy narratives that feature swelling music and melodramatic conversations, Juno’s discussions about abortion are straightforward, blunt, and reasonable.
 |
| Juno getting an ultrasound |
Yet after some deliberation, and actually going to an abortion clinic, Juno decides not to have an abortion. What changes her mind? When walking into the abortion clinic she has a conversation with a classmate who is standing outside protesting. Her classmate informs her that at this period in her pregnancy her “baby” has already grown fingernails, which seems to force Juno to reevaluate her decision. Ignoring not just the relevance of this fact, but the accuracy (fetuses develop fingernails between weeks ten and fifteen, while by Juno’s estimation she is in her ninth or tenth week), we at least see multiple discussions that influence the character’s thought process and lead her to her final decision.
But while Knocked Up was at least realistic in depicting the privileges that allows Alison to have and raise a child with as little stress as possible, Juno‘s portrayal of teen pregnancy creates a situation so ideal for its protagonist’s pregnancy that it borders on fantasy. After choosing not to have an abortion, Juno decides instead to give her baby up for adoption, and finds an attractive, white, upper-middle class couple looking to adopt her baby. That stroke of luck not only stretches credulity, it paints a far rosier picture of the adoption process than reality. In 2007, when Juno was released, 133,640 children in the United States were waiting to be adopted, including 1,674 in Minnesota, where the film takes place.
Of course, one way in which this remarkably easy adoption process is realistic is the role that white privilege plays, although this privilege is of course never acknowledged in the film. White babies are typically far more in demand than babies of color; of all adopted children in the United States in 2000, 64% were white, while white children made up only 40% of children in the Foster Care system. If Juno were black or hispanic, would it have been so easy to find a well-off couple to adopt her child? Statistically, no, and it is likely that her child would have ended up in the foster care system. In 2009 the median amount of time spent in foster care was 13.7 months, and over half of children that were removed from foster care were taken back in by their birth parents, compared to only 20% that were adopted.
The ease with which Juno finds a family to adopt her baby is steeped in privilege both realistic and otherwise, but that is not the only way that Juno’s pregnancy is made as easy as possible for the sake of the narrative. Juno is a high school junior during the course of the film, and makes no effort to hide her pregnancy in any way. We get no sense that she is ostracized, bullied, or shamed for her decision, either by her classmates or by the school itself. Nor do we ever see any indication that her pregnancy interferes with her school work. Considering that approximately 70% of pregnant teenagers drop out of school, it is fair to say that the miniscule impact that pregnancy has on Juno’s life bears little resemblance to the reality of teen pregnancy.
Knocked Up and Juno paint an unrealistically bright picture of how pregnancy can impact a woman’s life. Both films take advantage of privileges without acknowledging them and even invent privileges that their characters would likely not have in the real world. In doing so, they create situations in which abortion does not have to be seriously considered. By giving abortion short shrift these films allow viewers to forget how serious and important a woman’s right to choose is, and how serious the consequences would be for real women in the same situations as Juno and Alison if abortion were not an option. 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days makes a strong case for legal abortion by showing just how terrible it is in the real world to be faced with either having to bear a child or to obtain a legal abortion. The film stands in stark contrast to Juno and Knocked Up not only because it released in the same year as those two films, but because the film treats pregnancy and abortion as serious issues, not fun jokes.
Cristian Mungiu’s film is set in Romania in the late 1980s, when the country was still part of the Soviet Union. This is a very different setting than either Minnesota or Los Angeles circa 2007; milk is a luxury, gasoline is a rarity, and cigarettes are contraband. The protagonists of the film are college students, not mired in poverty or starving, but well off and stable. This disparity between what it means to be well off in the United States and what it means in the Soviet Union makes it clear how difficult living under Soviet rule was. Otilia is a young woman trying to help her friend Gabriela get an abortion. While for Juno this is as simple as making an appointment at a clinic and attempting to not be swayed by the lone, peaceful protester, for Gabriela it is much more complicated. She and Otilia must contact a man who performs abortions, make an appointment at a hotel, and borrow enough money from friends to pay for everything. Every step of the way they know that if they are caught they will be arrested and imprisoned.
Gabriela attempts to lie to the man performing the operation, claiming that she is in her second month, but he realizes that she is further along than that (she never says how far she is but we glean that the film’s title is referring to the actual answer). He refuses to perform the procedure after he realizes that Gabriela was lying and that she does not have as much money as he wants, but decides that in addition to the payment that he wants to have sex with Otilia. This is the sort of situation that women can find themselves in when legal abortion is not an option. Otilia is faced with the decision of either making her friend carry her fetus to term–which would result in the end of any sort of academic career and would likely lead to a life of poverty if the father refuses to support the child–or to prostitute herself for the sake of her friend. Otilia is raped so that she can help her friend, a circumstance that feels a universe away from the witty quips and hamburger phones that make up Juno’s life.
The procedure itself is dangerous and potentially life threatening. It involves the man inserting a probe filled with fluid into Gabriela’s vagina while she lies still from between two and forty-eight hours. The unspecified fluid induces a miscarriage, which causes Gabriela to bleed significantly as she births her stillborn fetus. The unsanitary location and lack of professional medical equipment make it likely that Gabriela will either bleed out or get an infection during the course of the procedure. However, in the film, the procedure works effectively and Otilia disposes of the fetus while Gabriela rests and recuperates.
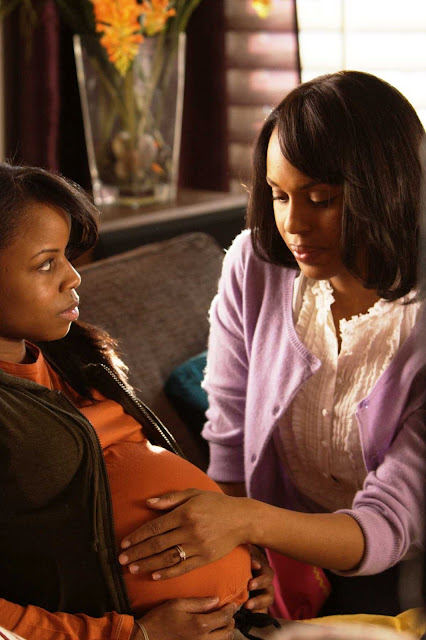
 |
| Gabriela and Otilia from 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days |
Cristian Mungiu does not depict Gabriela’s abortion as relatively free of incident because he wants to portray this sort of illegal abortion as easy or simple. There are enough traumatic moments throughout the film to reinforce how dangerous and awful a backdoor abortion can be. Rather, the abortion itself is free of incident because Mungiu is making it clear that this is normal. We see Gabriela and Otilia mention other women who have had abortions, and they only find this man because he was recommended to them by a friend. In this society, illegal abortions are as common as legal abortions are in our society. But instead of going to a hospital or a clinic to have the operation done, women in Romania had to find people willing to perform the procedure in hotel rooms late at night, with the threat of imprisonment hanging over their heads the whole time.
For Juno and Alison, the decision to have a child is not easy, but it is simple. There is deliberation, and there is drama, and both of them consider their options carefully—although Alison mostly does so offscreen—but their choices are either to have a safe, legal abortion, or to have a safe, complication-free pregnancy and birth with a happy ending that involves for Juno giving the child to a well-off, stable woman, and for Alison raising the child in a well-off, stable household. Both films create characters and situations that are as conducive as possible to happy, healthy pregnancy and birth, and in some instances even strain the boundaries of reasonable possibility.
4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days presents a character in a situation who has none of the advantages and privileges that Alison and Juno have. In our current political climate that seems intent on repealing every reproductive right women have gained over the last fifty years, it is important for us not to take the right to choose for granted, to treat it like a joke, or to discuss it with hushed tones and euphemisms, as if it is something embarrassing that no respectable, reasonable woman would do. By presenting abortion as the wrong choice, and pregnancy and birth as easy and spiritually fulfilling, movies like Juno and Knocked Up support the conservatives in the culture war, no matter how progressive they might seem to be. Movies with these messages are dangerous for women, because they drastically misrepresent reality, leaving it to low-budget foreign dramas to tell the truths that desperately need to be heard.
———-
Tom Houseman was born white, straight, male, cis, and rich. He has done a lot of work unpacking and understanding his many forms of privilege. He is far from perfect, but he is learning. He writes film reviews and analysis for
BoxOfficeProphets.com. If you want to officially like him, you can do so at
Facebook.com/tomhousemanwriting.